Quick Start
Overview
This guide demonstrates how to set up and run a microservice using the StackSaga framework with minimal configuration. It focuses on a common use case where a microservice communicates with multiple other microservices to fulfill a single business logic.
Basic implementation
Use Case: Placing an Order
In this scenario, we have a microservice called Order Service, which needs to interact with the following microservices to place an order successfully:
- Payment Service
-
Handles payment processing.
- Stock Service
-
Manages inventory checks and updates.
- User Service
-
Retrieves and verifies user information.
The goal is to demonstrate how the StackSaga framework simplifies the process of coordinating communication between these microservices to implement the business logic for order placement.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure the following: === Creating the orchestrator service
-
Java Development Environment: JDK 17 or higher is installed.
-
Database: Mysql or any database that supports stacksaga. (This example uses Mysql)
-
Microservices Setup: Basic implementations of Order Service, Payment Service, Stock Service, and User Service are available.
The steps are as follows.
Creating the orchestrator service
As the first step, let’s create the orchestrator service (order-service). It is nothing but a spring boot web application with mysql-database support.
Go to the spring initializr and create a new project with the following dependencies.
-
Spring Web
-
Lombok (for avoiding boilerplate code)
-
MySQL Driver (For using mysql database as the event-store)
Adding stacksaga dependencies and update the required configuration properties.
After creating the project, it is necessary to add the required stacksaga dependencies in the dependencies section.
- stacksaga-spring-boot-starter
-
The core of the framework.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.stacksaga</groupId>
<artifactId>stacksaga-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>- stacksaga-mysql-support
-
The Mysql database supports implementation for the framework.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.stacksaga</groupId>
<artifactId>stacksaga-mysql-support</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>Then update the required configuration properties in the applocation.yml or application.properties file.
spring:
application:
name: order-service (1)
stacksaga:
enable: true (2)
component-scan: demo.quickdemo.aggregators (3)
app-release-version: 1.0.0 (4)
datasource: (5)
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/stacksaga_event_store?createDatabaseIfNotExist=true
username: database_username
password: database_password
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver| 1 | The name of the application is required for stacksaga |
| 2 | Enable stacksaga framework |
| 3 | The package path of the aggregators that are localed in. |
| 4 | The application release version |
| 5 | The database configuration for accessing the mysql database as the event-store. |
See more,
-
stacksaga-spring-boot-starterconfiguration properties -
stacksaga-mysql-supportconfiguration properties
Creating an aggregator
Creating an Aggregator is one of the main steps in the stacksaga framework implementation. Because it is the container that holds the states of each execution’s data until the transaction is completed.
create the aggregator class in the demo.quickdemo.aggregators package with the fields that you want to store the data while the entire transaction.
- PlaceOrderAggregator.java
package demo.quickdemo.aggregators;
import lombok.*;
import org.stacksaga.Aggregator;
import org.stacksaga.SagaSerializable;
import org.stacksaga.annotation.SagaAggregator;
import org.stacksaga.annotation.SagaAggregatorVersion;
@SagaAggregator(
version = @SagaAggregatorVersion(major = 1, minor = 0, patch = 0),
name = "PlaceOrderAggregator",
sagaSerializable = PlaceOrderAggregatorSagaSerializable.class
)
@Getter
@Setter
public class PlaceOrderAggregator extends Aggregator {
private String orderId;
private double amount;
private String userId;
private boolean isPaid;
private String paymentId;
public PlaceOrderAggregator() {
super(PlaceOrderAggregator.class);
}
}
class PlaceOrderAggregatorSagaSerializable extends SagaSerializable<PlaceOrderAggregator> {
public PlaceOrderAggregatorSagaSerializable() {
this.put("Sample-1", new PlaceOrderAggregator());
}
}Creating executors
Create the executors in the demo.quickdemo.executors package.
For this quick-start example, four executors are created to make individual atomic executions to the relevant services.
-
PlaceOrderInitExecutor for order-service (itself)
-
GetUserDetailsExecutor for user-service
-
MakePaymentExecutor for payment-service
-
StockUpdateExecutor for stock-service
PlaceOrderInitExecutor
package demo.quickdemo.executors;
import demo.quickdemo.aggregators.PlaceOrderAggregator;
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
import org.stacksaga.ProcessStepManager;
import org.stacksaga.ProcessStepManagerUtil;
import org.stacksaga.RevertHintStore;
import org.stacksaga.annotation.SagaExecutor;
import org.stacksaga.core.SagaExecutionEventName;
import org.stacksaga.exception.RetryableExecutorException;
import org.stacksaga.exception.execution.NonRetryableExecutorException;
import org.stacksaga.executor.CommandExecutor;
import java.util.Random;
@SagaExecutor(
executeFor = "order-service",
value = "PlaceOrderInitExecutor"
)
public class PlaceOrderInitExecutor implements CommandExecutor<PlaceOrderAggregator> {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public ProcessStepManager<PlaceOrderAggregator> doProcess(
PlaceOrderAggregator currentAggregator,
ProcessStepManagerUtil<PlaceOrderAggregator> stepManager,
String idempotencyKey
) throws RetryableExecutorException, NonRetryableExecutorException {
// TODO: execute place order process here
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextLong(1000, 3000));
{
//updates the aggregator with the order id
currentAggregator.setOrderId(currentAggregator.getAggregatorTransactionId());
}
return stepManager.next(GetUserDetailsExecutor.class, () -> "INITIATED_ORDER");
}
@Override
public SagaExecutionEventName doRevert(NonRetryableExecutorException processException,
PlaceOrderAggregator finalAggregatorState,
RevertHintStore revertHintStore,
String idempotencyKey
) throws RetryableExecutorException {
// TODO: execute place order revert process here
return () -> "ORDER_CANCELLED";
}
}GetUserDetailsExecutor
package demo.quickdemo.executors;
import demo.quickdemo.aggregators.PlaceOrderAggregator;
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
import org.stacksaga.ProcessStepManager;
import org.stacksaga.ProcessStepManagerUtil;
import org.stacksaga.annotation.SagaExecutor;
import org.stacksaga.exception.RetryableExecutorException;
import org.stacksaga.exception.execution.NonRetryableExecutorException;
import org.stacksaga.executor.QueryExecutor;
import java.util.Random;
@SagaExecutor(
executeFor = "user-service",
value = "GetUserDetailsExecutor"
)
public class GetUserDetailsExecutor implements QueryExecutor<PlaceOrderAggregator> {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public ProcessStepManager<PlaceOrderAggregator> doProcess(
PlaceOrderAggregator currentAggregator,
ProcessStepManagerUtil<PlaceOrderAggregator> stepManager,
String idempotencyKey
) throws RetryableExecutorException, NonRetryableExecutorException {
// TODO: Get user details from user-service
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextLong(1000, 3000));
{
//updates the aggregator with the user details
currentAggregator.setUserId("mafei");
}
return stepManager.next(MakePaymentExecutor.class, () -> "PLACED_ORDER");
}
}MakePaymentExecutor
package demo.quickdemo.executors;
import demo.quickdemo.aggregators.PlaceOrderAggregator;
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
import org.stacksaga.ProcessStepManager;
import org.stacksaga.ProcessStepManagerUtil;
import org.stacksaga.RevertHintStore;
import org.stacksaga.annotation.SagaExecutor;
import org.stacksaga.core.SagaExecutionEventName;
import org.stacksaga.exception.RetryableExecutorException;
import org.stacksaga.exception.execution.NonRetryableExecutorException;
import org.stacksaga.executor.CommandExecutor;
import java.util.Random;
@SagaExecutor(
executeFor = "payment-service",
value = "MakePaymentExecutor"
)
public class MakePaymentExecutor implements CommandExecutor<PlaceOrderAggregator> {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public ProcessStepManager<PlaceOrderAggregator> doProcess(
PlaceOrderAggregator currentAggregator,
ProcessStepManagerUtil<PlaceOrderAggregator> stepManager,
String idempotencyKey
) throws RetryableExecutorException, NonRetryableExecutorException {
// TODO: execute payment process here
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextLong(1000, 3000));
{
//updates the aggregator with the payment id
currentAggregator.setPaymentId("payment-1");
currentAggregator.setPaid(true);
}
return stepManager.next(StockUpdateExecutor.class, () -> "MADE_PAYMENT");
}
@Override
public SagaExecutionEventName doRevert(NonRetryableExecutorException processException,
PlaceOrderAggregator finalAggregatorState,
RevertHintStore revertHintStore,
String idempotencyKey
) throws RetryableExecutorException {
// TODO: execute payment revert process here
return () -> "PAYMENT_REFUNDED";
}
}StockUpdateExecutor
package demo.quickdemo.executors;
import demo.quickdemo.aggregators.PlaceOrderAggregator;
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
import org.stacksaga.ProcessStepManager;
import org.stacksaga.ProcessStepManagerUtil;
import org.stacksaga.RevertHintStore;
import org.stacksaga.annotation.SagaExecutor;
import org.stacksaga.core.SagaExecutionEventName;
import org.stacksaga.exception.RetryableExecutorException;
import org.stacksaga.exception.execution.NonRetryableExecutorException;
import org.stacksaga.executor.CommandExecutor;
import java.util.Random;
@SagaExecutor(
executeFor = "stock-service",
value = "StockUpdateExecutor"
)
public class StockUpdateExecutor implements CommandExecutor<PlaceOrderAggregator> {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public ProcessStepManager<PlaceOrderAggregator> doProcess(
PlaceOrderAggregator currentAggregator,
ProcessStepManagerUtil<PlaceOrderAggregator> stepManager,
String idempotencyKey
) throws RetryableExecutorException, NonRetryableExecutorException {
// TODO: execute stock update process here
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextLong(1000, 3000));
return stepManager.complete(() -> "STOCK_UPDATED");
}
@Override
public SagaExecutionEventName doRevert(NonRetryableExecutorException processException,
PlaceOrderAggregator finalAggregatorState,
RevertHintStore revertHintStore,
String idempotencyKey
) throws RetryableExecutorException {
// TODO: execute stock revert process here
return () -> "STOCK_REVERTED";
}
}Creating Endpoint
- PlaceOrderDto
package demo.quickdemo.dto;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
public class PlaceOrderDto {
@Data
public static class Request {
private double amount;
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public static class Response {
@JsonProperty("order_id")
private final String orderId;
}
}- PlaceOrderController
package demo.quickdemo.controller;
import demo.quickdemo.aggregators.PlaceOrderAggregator;
import demo.quickdemo.dto.PlaceOrderDto;
import demo.quickdemo.executors.PlaceOrderInitExecutor;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.stacksaga.core.SagaTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/order")
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class PlaceOrderController {
private final SagaTemplate<PlaceOrderAggregator> placeOrderAggregatorSagaTemplate;
@PostMapping("/place")
public PlaceOrderDto.Response placeOrder(@RequestBody PlaceOrderDto.Request request) {
final PlaceOrderAggregator placeOrderAggregator = new PlaceOrderAggregator();
placeOrderAggregator.setAmount(request.getAmount());
final String orderId = this.placeOrderAggregatorSagaTemplate.process(placeOrderAggregator, PlaceOrderInitExecutor.class);
return new PlaceOrderDto.Response(orderId);
}
}Run and Test
Run the application and make a place order request via Postman and get the order_id (transaction-id).
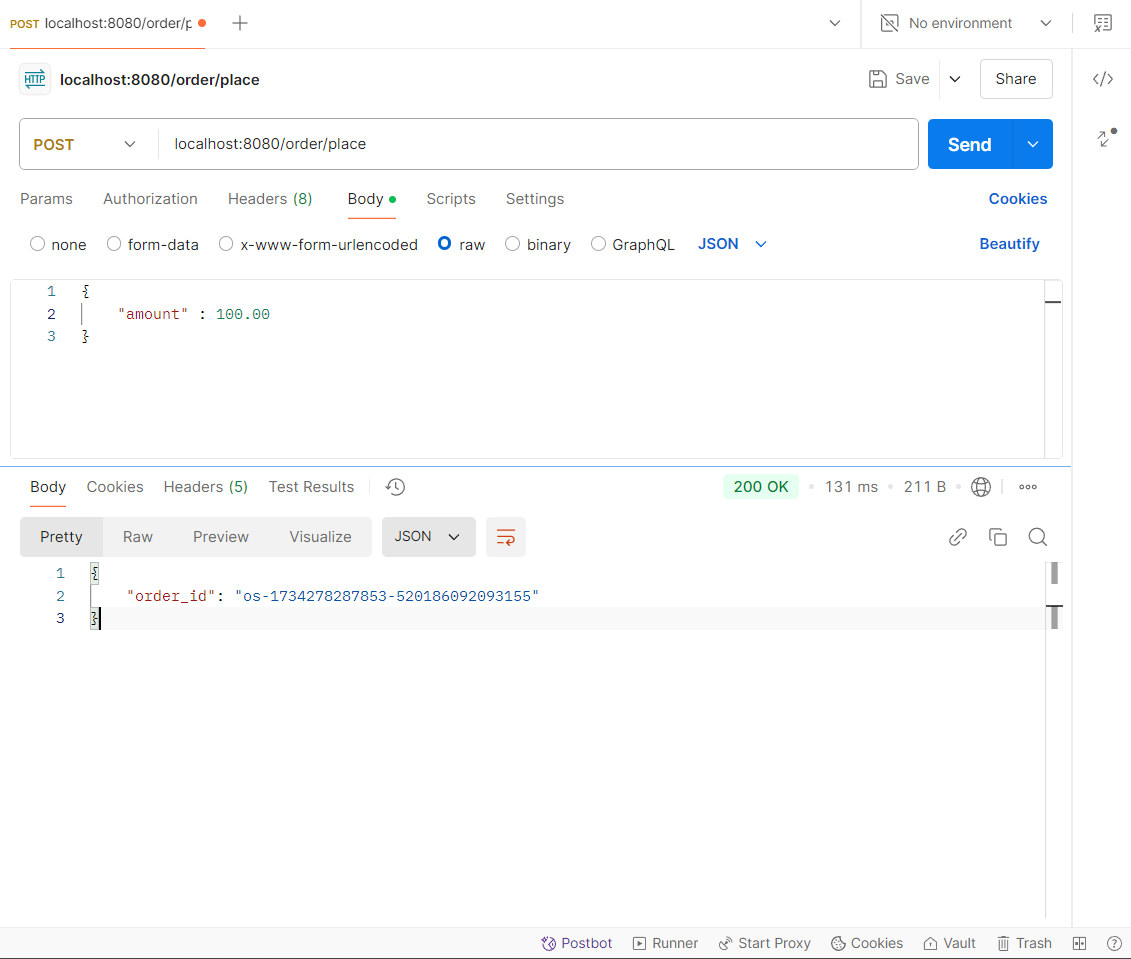
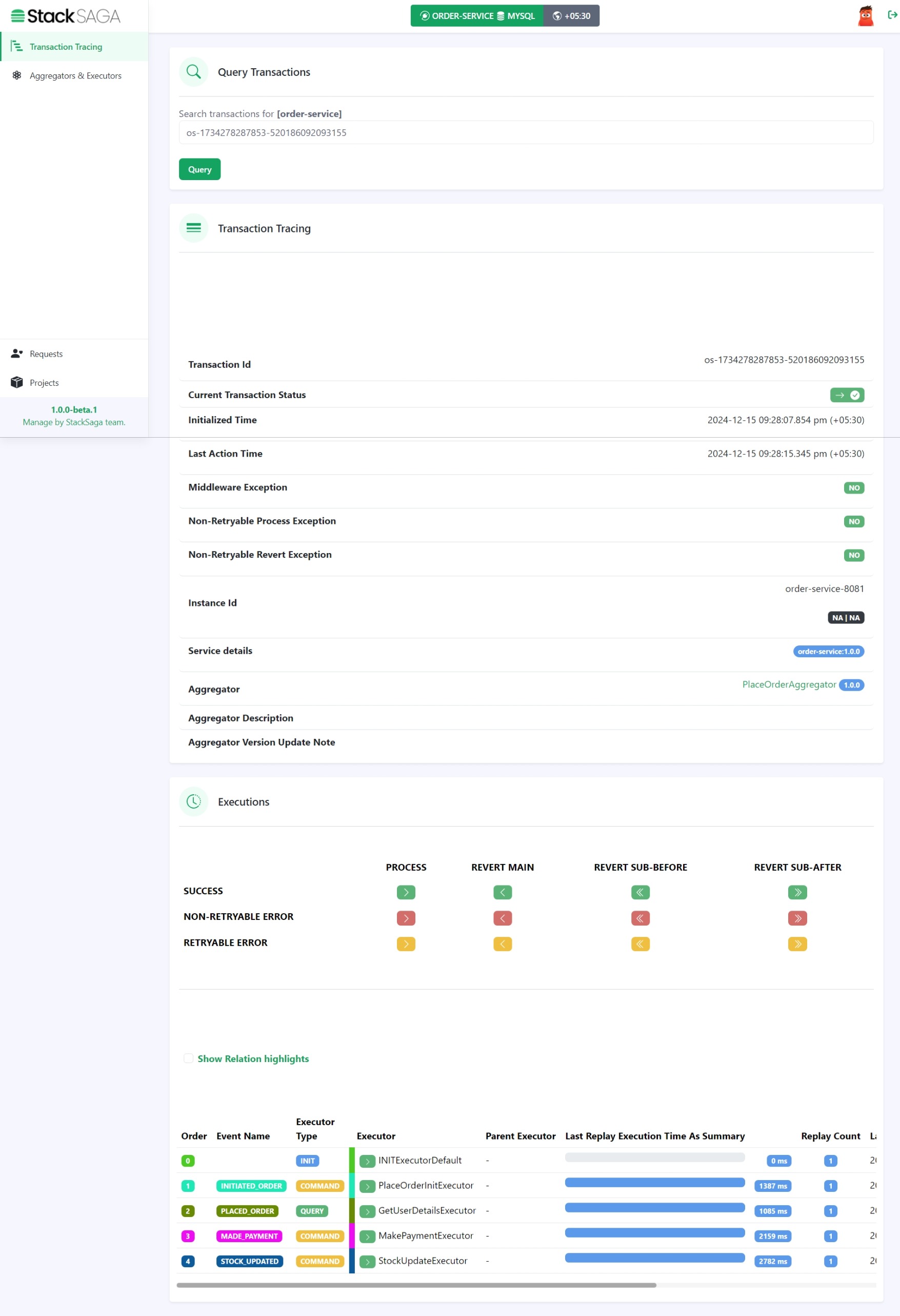
After connecting the Stacksaga Cloud-Window successfully, go to the transaction-tracing page and enter the order_id and see the transaction tracing details.
Congratulations!
You have successfully implemented the major part of the quick demo.
It was about the successful scenario.
Let’s move on to the next part.
It focuses on Transaction Retrying.
Retrying with StackSaga Agent
As per the stacksaga architecture, we have to deploy an agent-service for retrying the transaction for the target orchestrator service (order-service).
The steps are as follows:
Adding StackSaga Agent Dependency
Add the stacksaga-agent-mysql-starter dependency to the pom.xml file.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.stacksaga</groupId>
<artifactId>stacksaga-agent-mysql-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>
According to this example, we have used mysql database implementation for the event store.
Therefore, the agent dependency should be the stacksaga-agent-support-mysql.
If you have used another database implementation, please change the dependency accordingly.
|
Customize the configuration
After adding the dependency, in the main class of the application, replace StackSagaAgentRunner class with SpringApplication.
public static void main(String[] args) {
//replace StackSagaAgentRunner with SpringApplication
StackSagaAgentRunner.run(QuickStartApplication.class, args);
}And then update the application.yml file as follows with your configuration.
server:
port: 5566 (1)
spring:
profiles:
active: eureka (2)
application:
name: order-service-agent-eureka (3)
datasource: (4)
username: username
password: password
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/order-service
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
stacksaga:
agent:
retry-batch-size: 10000 (4)
target-service: order-service (5)
target-service-host: order-service (6)
act-master-as-slave: true (7)
retry-pool:
pool-size: 10 (8)
eureka:
instance-type: master (9)
token-range-update-delay: 10000 (10)
token-range-update-initial-delay: 10000 (11)
token-range-valid-duration: 150000 (12)
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka/ (13)